Skeletal System
Imagine a building without its steel skeleton. It would just be a mass of cement. Similarly, the human body without a skeletal system will just be a bag of muscles, without any shape or structure. The human skeletal system is made up of different types of bones and joints.
The human skeletal system is a framework that gives proper shape and provides protection to the body.
Formation of Human Skeletal System
The process by which bones are formed is called as ossification. Ossification is a life-long process. There are two types of ossification:
Endochronal Ossification: When the fetus is in the early phase of development, it has a skeleton made up of cartilages. These cartilages develop gradually into bones, by the process of endochronal ossification. Bones like femur (thigh bone) are formed from this process.
Intramembranous Ossification: Here, bones are formed from a connective bone tissue made of cells called mesenchyme cells. Skulls bones are formed by this process.
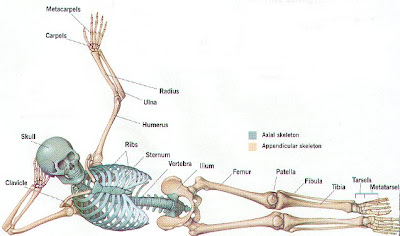
Organization of Human Skeletal System
The human skeletal system is perpendicularly symmetrical in nature. It consists of the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
Functions of Human Skeletal System
Support: The human skeletal system gives proper shape to the body. It is a framework that supports body organs and muscles.
Body Movements: The joints present between different bones allow body movements.
Producing Stem Cells: Stem cells are produced in the bone marrow, which is a part of the skeleton. These stem cells further develop into RBCs, WBCs and platelets.
Storage of Calcium and Iron: Bones can store calcium and iron. About 99% of the calcium in the body is stored in bones. They help in iron and calcium metabolism.
Role in Endocrine System: Osteocalcin is the hormone which regulates fat deposition and glucose. This hormone is released by the bones.
Protection: It's the most important function of the human skeletal system. The following table illustrates the organs and the bones which protect them.
Nervous System
The nervous system is closely connected to the brain, and is responsible for body movements. It works together with various glands in the body to maintain the functions of other systems for agility and strength.
Reference: www.zell-v.com
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular/circulatory system transports food, hormones, metabolic wastes, and gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide) to and from cells. Components of the circulatory system include:
Blood: consisting of liquid plasma and cells
Blood vessels (vascular system): the "channels" (arteries, veins, capillaries) which carry blood to/from all tissues. (Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins return blood to the heart. Capillaries are thin-walled blood vessels in which gas/ nutrient/ waste exchange occurs.)
Heart: a muscular pump to move the blood
There are two circulatory "circuits": Pulmonary circulation, involving the "right heart," delivers blood to and from the lungs. The pulmonary artery carries oxygen-poor blood from the "right heart" to the lungs, where oxygenation and carbon-dioxide removal occur. Pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood from tbe lungs back to the "left heart." Systemic circulation, driven by the "left heart," carries blood to the rest of the body. Food products enter the sytem from the digestive organs into the portal vein. Waste products are removed by the liver and kidneys. All systems ultimately return to the "right heart" via the inferior and superior vena cavae.
A specialized component of the circulatory system is the lymphatic system, consisting of a moving fluid (lymph/interstitial fluid); vessels (lymphatics); lymph nodes, and organs (bone marrow, liver, spleen, thymus). Through the flow of blood in and out of arteries, and into the veins, and through the lymph nodes and into the lymph, the body is able to eliminate the products of cellular breakdown and bacterial invasion.
Muscular System
Body movement is controlled by a network of over 600 muscles. These muscles make up the muscular system. All muscle tissue doesn’t have the same appearance. However, all muscles have one unique characteristic, the ability to shorten, or contract, this ability allows body movement.
There are three types of muscles in your body: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles:
· Skeletal muscles move the bones of the skeleton, they are attached to bones by tough bands of tissue called tendons, they are voluntary, and i.e. person has control over them.
· Smooth muscles form the walls of many internal organs such as the stomach, their action is involuntary, and you have no control over them.
· Cardiac muscle has character of skeletal and smooth muscles, but it is regarded as a distinct kind of muscle. Cardiac muscle is also involuntary muscle. It pumps blood at an average of 70 times/min. 40 million times a year for a life time.
Information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only; it is not intended as a substitute for advice from your own medical team or any form of advertisment. The information on this blog is not to be used for diagnosing or treating any health concerns you may have - please contact your physician or health care professional for all your medical needs.









ReplyDeleteIni Kenapa orang-orang Selalu Mengira Saya 10 tahun Lebih Muda KLIK DISINI
phytogreen | zell v platinum plus | zell v phytogreen | zell v | placenta domba | zell v price | zell v placenta | zell v product | cream pemutih |suntik stem cell | plasenta rusa | placenta kosmetik | suntik placenta | produk placenta | zell v gold | kosmetik placenta | zel-v plus | suntik placenta domba | suntik placenta di wajah | pemutih wajah placenta | placenta pemutih wajah |pemutih placenta | terapi stem cell | tanam benang | zell v platinum plus | zell v | placenta domba
ReplyDeleteNice information, many thanks to the author. It is incomprehensible to me now, but in general, the usefulness and significance is overwhelming. Thanks again and good luck!
zell v | placenta domba | zell v price | zell v placenta | zell v sheep placenta | zell v product | cream pemutih |suntik stem cell | plasenta rusa | placenta kosmetik | suntik placenta | produk placenta | injeksi placenta | kosmetik placenta | placenta injeksi | suntik placenta domba | suntik placenta di wajah | pemutih wajah placenta | placenta pemutih wajah |pemutih placenta | terapi stem cell | tanam benang | zell v platinum plus| phytogreen | zell v phytogreen | zell v phytogreen | zell v phytogreen